why liver cannot utilize ketone bodies Why ketone diet ketogenic metabolic autism ketones brain role blood bacon considerations friend part ketoacidosis barrier
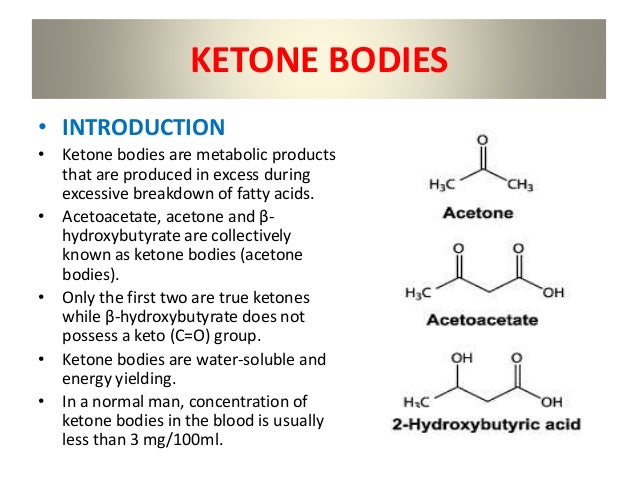
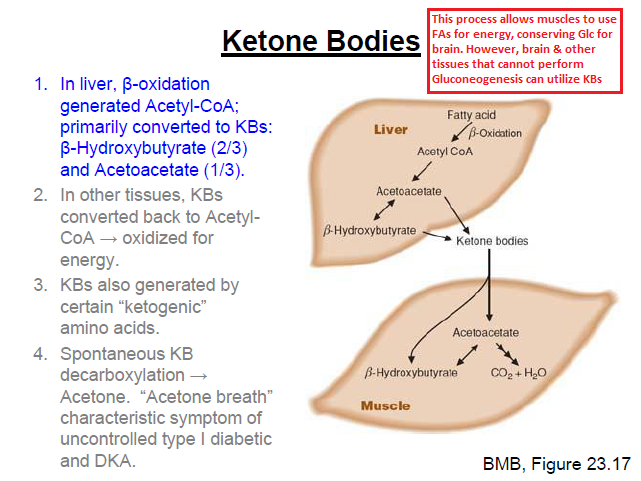
Ketogenesis: Steps, Pathway, Significance Ketogenesis is a metabolic process that occurs in the liver and is responsible for the production of ketone bodies. This process is essential for maintaining energy levels in the body when glucose levels are low, such as during fasting, or when carbohydrate intake is reduced, such as in a low-carbohydrate diet. Ketone bodies are produced from the breakdown of fatty acids and can be used as an alternative source of energy by the brain and other organs. The process of ketogenesis can be broken down into several steps. The first step is the breakdown of fatty acids, which occurs in the liver. Fatty acids are broken down into two-carbon units called acetyl-CoA. These units then enter the Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle, where they are metabolized to produce energy in the form of ATP. The second step in ketogenesis is the production of ketone bodies. Acetyl-CoA molecules that are not used in the Krebs cycle are converted into ketone bodies. There are three types of ketone bodies that are produced: acetone, acetoacetate, and beta-hydroxybutyrate. Acetone is a volatile molecule that is excreted in the breath and urine, while acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate are used as an energy source by the body. The third step in ketogenesis is the transport of ketone bodies to other tissues. Ketone bodies are transported by the bloodstream to other organs, such as the brain, heart, and skeletal muscles, where they can be used as an energy source. The brain, in particular, relies heavily on ketone bodies for energy during periods of low glucose availability. The significance of ketogenesis lies in its ability to provide the body with an alternative source of energy when glucose levels are low. This is especially important for the brain, which cannot use fatty acids for energy and relies on glucose as its primary source of fuel. In addition, ketogenesis has been shown to have therapeutic benefits for certain conditions, such as epilepsy and type 2 diabetes. In conclusion, ketogenesis is a metabolic process that occurs in the liver and is responsible for the production of ketone bodies. The process involves the breakdown of fatty acids to produce acetyl-CoA, which is then converted into ketone bodies. These ketone bodies are then transported to other tissues, where they can be used as an energy source. The significance of ketogenesis lies in its ability to provide the body with an alternative source of energy when glucose levels are low, and its therapeutic benefits for certain conditions.
If you are searching about USMLE Notes - Ketone bodies are produced in the liver and can be… you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Pictures about USMLE Notes - Ketone bodies are produced in the liver and can be… like THE ROLE OF THE KETOGENIC DIET IN AUTISM OR WHY BACON IS YOUR FRIEND, Researchers have made a discovery about how disease pathogenesis in the and also THE ROLE OF THE KETOGENIC DIET IN AUTISM OR WHY BACON IS YOUR FRIEND. Here you go:
USMLE Notes - Ketone Bodies Are Produced In The Liver And Can Be…
 usmle-notes.tumblr.comketone liver produced usmle mitochondrial peripheral ketones mitochondria tissues
usmle-notes.tumblr.comketone liver produced usmle mitochondrial peripheral ketones mitochondria tissues
Researchers Have Made A Discovery About How Disease Pathogenesis In The
 debuglies.comketone bodies liver made body fatty disease regulated nafld pathogenesis researchers discovery nonalcoholic fats slideshare protect crawford scarring said fuels
debuglies.comketone bodies liver made body fatty disease regulated nafld pathogenesis researchers discovery nonalcoholic fats slideshare protect crawford scarring said fuels
Ketone Bodies Usage And Liver Fed State Formation In Liver Part2 - YouTube
 www.youtube.comKetogenesis: Steps, Pathway, Significance
www.youtube.comKetogenesis: Steps, Pathway, Significance
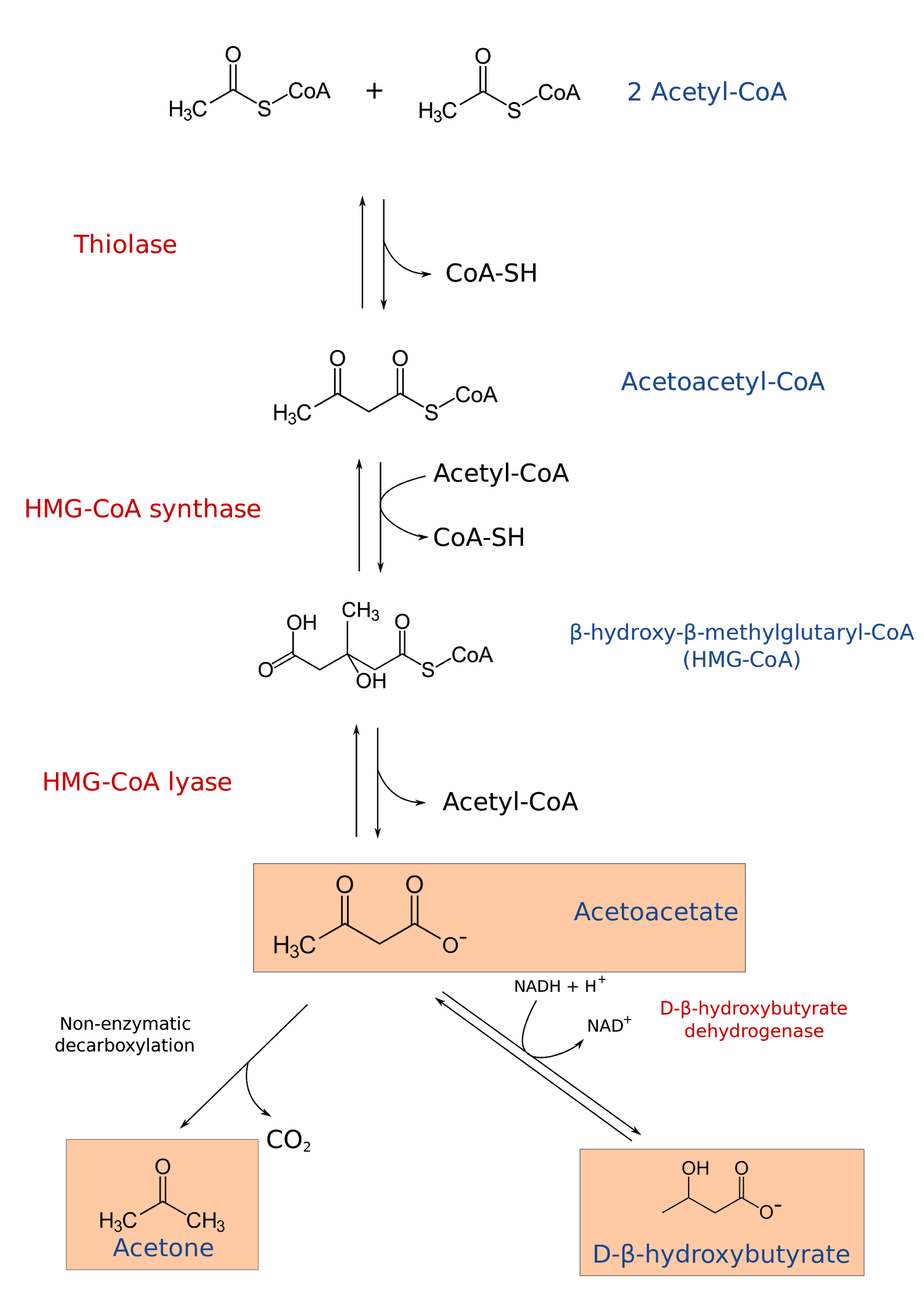 byjus.comketogenesis ketogenic ketosis ketoacidosis acids glucogenic ketone keto coa pathway corpos cetonicos bodies liver acetone hydroxybutyrate acyl
byjus.comketogenesis ketogenic ketosis ketoacidosis acids glucogenic ketone keto coa pathway corpos cetonicos bodies liver acetone hydroxybutyrate acyl
THE ROLE OF THE KETOGENIC DIET IN AUTISM OR WHY BACON IS YOUR FRIEND
 corticalchauvinism.comwhy ketone diet ketogenic metabolic autism ketones brain role blood bacon considerations friend part ketoacidosis barrier
corticalchauvinism.comwhy ketone diet ketogenic metabolic autism ketones brain role blood bacon considerations friend part ketoacidosis barrier
Why ketone diet ketogenic metabolic autism ketones brain role blood bacon considerations friend part ketoacidosis barrier. The role of the ketogenic diet in autism or why bacon is your friend. Ketogenesis ketogenic ketosis ketoacidosis acids glucogenic ketone keto coa pathway corpos cetonicos bodies liver acetone hydroxybutyrate acyl